NLP125 Topics
Spell Checkers
1. What is Python?
Joseph- One of many coding languages, simple and uses words.
2. What does a “library” in Python mean?
Joseph- A collection of code that makes everyday tasks more efficient
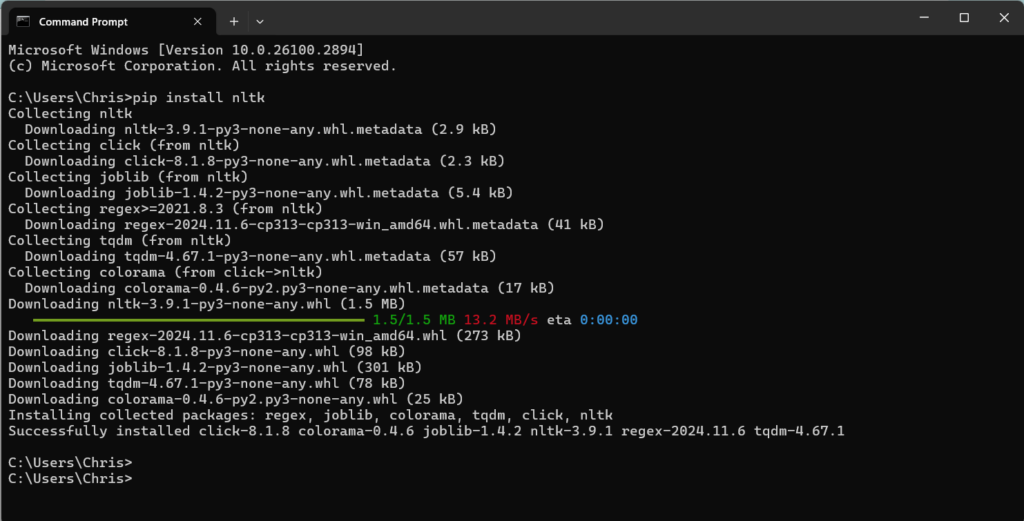
3. Attach a screenshot to show you installed NLTK.
Christian- Python Installed
CALL Tools – Duolingo
Identify one CALL tool that you could try out. Spend at least 10 minutes trying out the tool. Possible examples include, but are not limited too, DuoLingo, Mango Languages, Babble, Rosetta Stone, etc. What type of feedback does the tool give? Is it individualized feedback? How does the tool handle clozes? Does it allow multiple possibly correct answers? Does the tool allow you to work on, around or through the language?
After spending 10 minutes using DuoLingo, it was a positive experience overall. The application gives feedback and highlights mistakes. The feedback is not personalized but it does correct your errors efficiently. The responses to your errors are mostly digital and not individualized to a person but very informative when you need to understand what you are doing wrong.
DuoLingo uses fill-in-the-blank exercises on clozes and allows for many right answers depending on context. I feel like DuoLingo tries to work on, around, and through language challenges through information and exercises.

Searching and Googling
Langfun Tech is hiring an office manager. In their interview, they talk about doing the searching type tasks. Out of the tools: Tableau, Excel, a CRM, AntConc, MaxQDA, and Weka, which would you recommend and why?
1. They want to create a map of the US, showing the geographic locations/concentrations of their customers.
Tableau Would most likely be best
2. Langfun wants to keep track of all the people that have called them and whether or not they become customers.
A CRM would be best in this case
3. Langfun wants to track how many contracts they have issues over the past year and months, and which were for what service category.
Excel for data tracking and categorical data entries
4. Langfun has focus group data from potential customers and they want to analyze it to look for customer preferences.
MaxQDA or AntConc would be best in this case
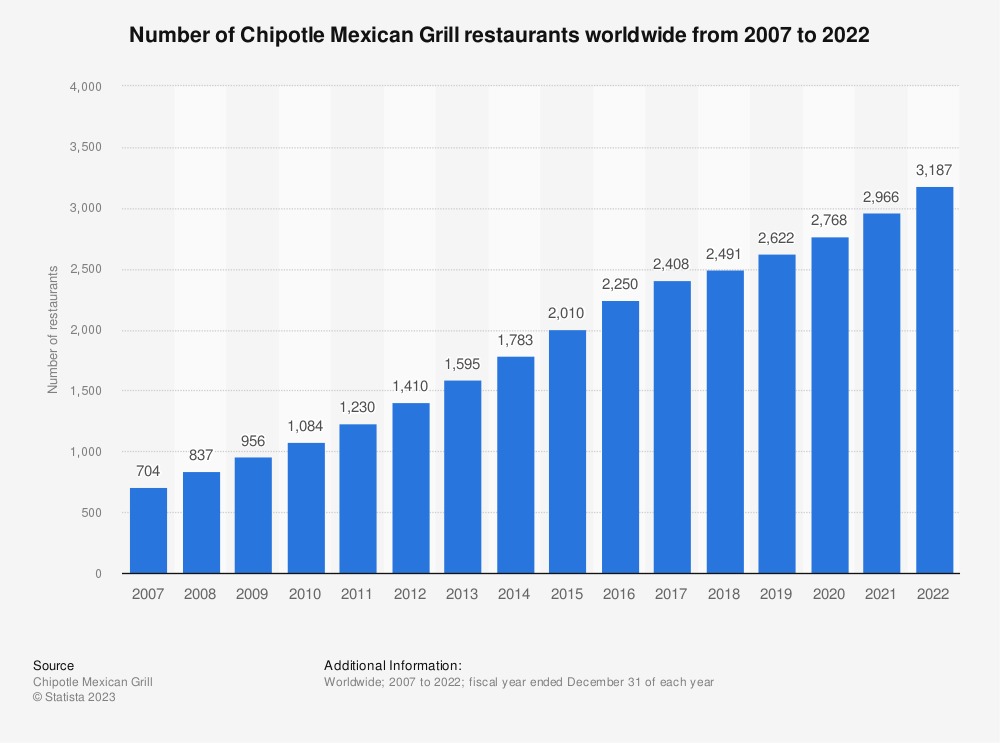
Corpus Linguistics
Pizza hut was only used in 2010's on the COCA Website
Chipotle had a frequency of 1171, most frequent in the 2010's.
Research Question:
How did the frequency of mentions and customer engagement with Pizza Hut and Chipotle evolve in the 2010s, and what can this tell us about changing consumer preferences?
Methodology and Data Collection:
To explore this, I analyzed search trends and social media mentions of Pizza Hut and Chipotle over the course of the 2010s. Data was collected from Google Trends, social media sentiment analysis, and public reports on restaurant sales. The analysis focused on frequency of mentions, sentiment, and notable events affecting both brands, such as menu innovations or marketing campaigns.
Findings:
Pizza Hut experienced a steady decline in search interest from 2010 to 2019, with a significant drop in 2017, reflecting a decrease in consumer engagement. In contrast, Chipotle saw a surge in mentions in the early part of the decade, particularly after 2015, following the brand's recovery from its food safety crisis. By 2019, Chipotle’s social media mentions had increased by 40%, while Pizza Hut's engagement dropped by 25% from its 2010 peak.
Discussion:
The findings suggest that Chipotle's focus on healthier, customizable menu options and its response to crisis management may have contributed to its rise in popularity. In contrast, Pizza Hut struggled to maintain relevance in a market increasingly focused on fast-casual dining and healthier eating habits. These trends highlight a broader cultural shift towards healthier, more transparent food choices, impacting traditional fast food chains.
Conclusion:
Document classification
Reflect on the following question: You’ll have to think about how to train the machine. What kind of data did you include in your training dataset and why? What other kind of data could have been helpful but maybe you couldn’t get in the short-term/for free? Your group may, in some cases, search for photograph sets. One possibility to get large data sets is to convert YouTubes into clips. Did your model work well for what you wanted? In what instances might your model not work very well? Include the link to your project.
Overall, the training of the dataset required 2 paths. Pictures of many cats and many animals that were not cats were uploaded to create the two classifications. The model worked great and was able to distinguish cats from other animals easily. The model may not work very well if similar animals are shown. Our model is linked below.
Chatbot Creation for Business Ventures
Identify a Product: Choose a product that appeared on Shark Tank and is sold on both Amazon and the company’s website. Market Analysis: Briefly analyze the product’s online sales channels and identify how a chatbot could improve customer interaction and sales. Design a Prototype: Using the selected tool, create a basic chatbot prototype that can guide customers through the purchasing process. Include a screenshots and/or a link to your prototype. Implementation Overview: Outline how this chatbot could be integrated into the product’s sales strategy. Reflect on the process of designing the chatbot and its potential impact on sales and customer engagement.
The customer support for a wide variety of products could be improved with chat bot integration, not just those from shark tank. Online sales would be conducted through the company itself or the product may be sold through other vendors.
Below are ways that a product could implement this chatbot to generate sales and the tools and resources used to do so.
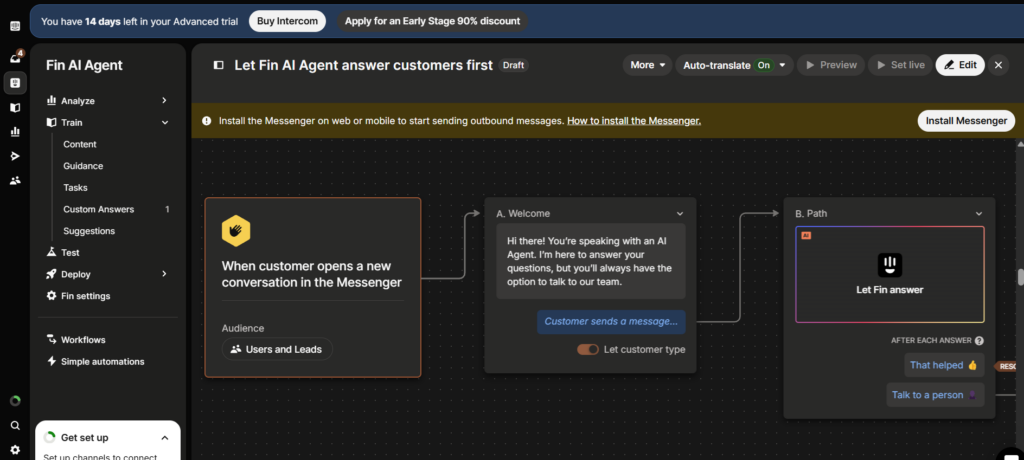
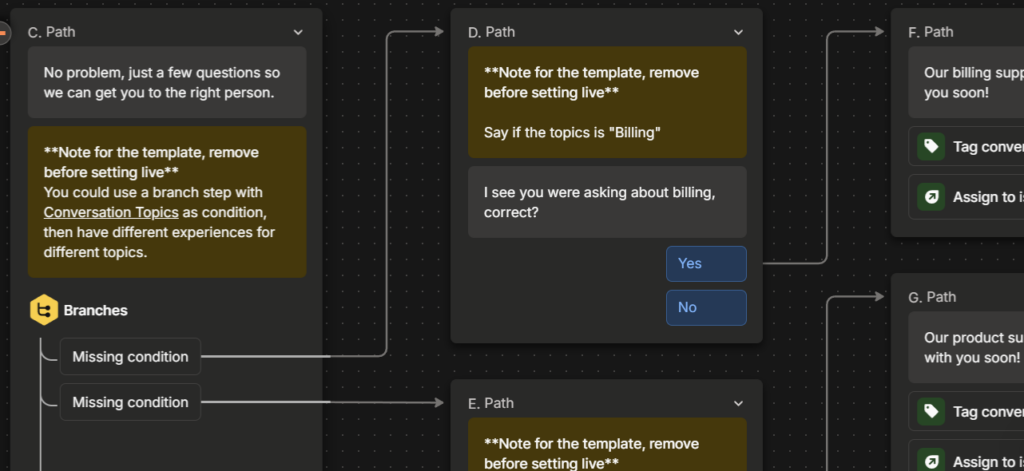
Using resources from Intercom, it was easy to create a drag and drop simple workflow design for a companies chatbot to use to answer questions or help in sales. Customers could engage easier with a representative and have better access to product merchandising.
Machine Translation Guideline Video
https://ai.invideo.io/watch/PCZ0Qn5QBGK
I. Introduction
-
Purpose of the Policy: AI and LLM technology is becoming increasing popular. Regulations and standards for use and citation are necessary for proper implementation in academic and business settings.
-
Scope: These guidelines apply to students, faculty, and administration in regards to their work and documentation produced.
II. Definitions
-
Generative AI: This policy is applicable to LLMs, Generative AI tools, and any form of technology that utilizes datasets to make informed or generative content.
-
Key Terms: An LLM is defined as a large language model. Generative AI is defined as models that use data to generate content in response to prompting. Bias is the tendency of the dataset to drift towards commonalities found in the training data.
III. Ethical Principles
-
Integrity and Honesty: Students must disclose the use of AI in assignments and coursework submitted or presented. Unoriginal ideas or inspiration gained from AI should be properly disclosed and cited as well. Any AI tool used without proper originality or citation will be held accountable for plagiarism.
-
Equity and Accessibility: All Students must have equal access to modern LLM’s and AI tools while also taking action to monitor bias in models
-
Privacy and Security: DO NOT give personal or important information to LLM or AI models as privacy and storage of information cannot be ensured.
IV. Guidelines for Use
-
Educational Use Cases: Generative AI can be used as brainstorming or information gathering tools but not as an entity to create an entire assignment from scratch.
-
Prohibited Uses: Prohibited uses include tests and exams as well as uncited uses in any form of submitted work.
-
Collaboration and Sharing: Shared material must be established as AI generated but is permitted
V. Responsibilities
-
Students: Students are responsible for disclosing AI generated content versus self creation
-
Teachers and Staff: Educators should provide guidance on proper use of AI to learn and create content
-
Administration: Administration should provide educational content to monitor and improve AI use in teachers and students
VI. Monitoring and Compliance
-
Monitoring Use: Monitoring use will be up to the teacher’s choice and review will be conducted by teachers and the administration.
-
Handling Violations: Breaches of the policy will be handled the same as plagiarism
VII. Support and Resources
-
Training and Education: Students and staff will have presentations held to show proper AI use and ethics with free resources
-
Technical Support: Basic support for AI tools will be given from IT at the school
VIII. Review and Update
-
Policy Review Schedule: This policy will be reviewed before the start of the new academic year, each year.
-
Feedback Mechanism: Students, Staff, and Faculty can provide feedback at school board meetings.